SQL Server functions, and
wanting to get a greater understanding of which functions are available
and how they can help improve the efficiency and facility of SQL
routines. Using system functions can help remove unwanted inefficiencies
in code, such as loops, nested loops and string-based field
manipulation. The functions available in SQL Server can tie in well with
business logic, enabling the developer to write better-suited
algorithms to support business requirements.
Functions in SQL Server -
one for statistical aggregation (VARP), one for English phonics
(SOUNDEX), and one for ranking and grouping (NTILE). It will also
provide an overview of the RANK and DENSE_RANK functionality to
complement the exploration of NTILE. Hopefully by seeing how useful just
a few functions can be, this article will encourage you to find out
more about system functions in SQL Server, and at the bottom of the
article are a number of links to the Books Online documentation on
non-user-defined functions.
As every data professional knows, some functions are used far more
than others - commonly SUM and COUNT. However SQL Server ships with a
wide variety of different functions, and these can be used in many
different contexts. For those of you of a mathematical or statistical
persuasion, it may interest you to know that SQL Server supports a wide
variety of statistical aggregation and calculation functions, together
with a number of mathematical and algebraic functions that can assist
in, for example finance calculations, often taking the place of more
complex and inefficient code.
VARP
Consider the following example to calculate the variance of a set of
temperature values. Here we first define a test table with some
temperature readings taken on different occasions for some major cities:
CREATE TABLE dbo.temperatureTable (
uqid INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
location VARCHAR(10),
locationCode TINYINT,
TemperatureA FLOAT,
TemperatureB FLOAT,
TemperatureC FLOAT,
TemperatureD FLOAT )
INSERT INTO dbo.temperatureTable (
location, locationCode, TemperatureA, TemperatureB, TemperatureC, TemperatureD )
VALUES ( 'London', 3, 19.6, 8.2, 16.4, 11.1 ),
( 'Paris', 7, 10.5, 20.2, 21.3, 18.0 ),
( 'Madrid', 4, 31.1, 28.3, 26.3, 28.7 ),
( 'Moscow', 9, -13.5, -12.0, -16.9, -0.3),
( 'Luxembourg', 6, 8.3, 5.5, 7.1, 9.9 )
Let us now say that we wish to compute the average deviation from the
mean for each city in our test table. That is, we wish to find out how
far away from the average, on average, each temperature reading is
within the appropriate category (location). However, we cannot simply
calculate the deviation by taking each reading and subtracting or adding
the mean, since this will give us a range of values that are mixed
positive and negative and by definition will cancel each other out. We
must instead use a different method of measuring the deviation. There
are three commonly used - absolute deviation, which is the deviation
from the mean with the sign (minus or plus) disregarded; the variance,
in which each deviation is squared to obtain a positive number (be aware
that -x^2 = x^2 for all positive natural numbers x in X) - and standard
deviation, which is simply defined as the average deviation, as
computed by variance (in other words, the square root of the variance).
So to be more precise, variance, mathematically, is defined as the
sum of the squared distances of each member of a set of numbers from the
mean (average) of that set of numbers, divided by the number of
members. So, in the example above, we might wish to know the mean
temperature in Moscow based on the information available, and the
variance of this set of data as our chosen measure of variation in
temperature. Because of the peculiarity of my example having a set of
data spread across columns rather than in a single column, we have an
opportunity to first UNPIVOT the data then use AVG and VARP to get this
information, like so:
SELECT location, AVG(Temperature) [averageTemp], ROUND(VARP(Temperature),2) [varTemp]
FROM (
SELECT location, TemperatureA, TemperatureB, TemperatureC, TemperatureD
FROM dbo.temperatureTable ) p
UNPIVOT
( Temperature FOR City IN
( TemperatureA, TemperatureB, TemperatureC, TemperatureD ) ) AS u
GROUP BY location
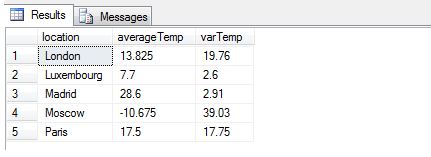
As you can see from this result, it might be better to use STDEV (or
STDEVP) to gain a more accurate measure of the true variance, as 39.03
is clearly a poor figure to indicate variance in degrees Celsius, since
it exceeds the range of values. In statistics, for precisely this
reason, standard deviation is the preferred variance measure as the
square root of the variance provides a linear relationship instead of an
exponential one. It's worth noting that SQL Server exhibits some odd
behavior here - although SQRT(VARP(expression)) is logically equivalent
to STDEVP(expression), interestingly and I suspect due to rounding,
truncation or arithmetic errors to do with SQRT, the two values are NOT
identical when computed in SQL Server - they vary by a small amount.
Variance still has its uses in mathematical circles, for example when
working out the total variance of uncorrelated variables, and other
matters familiar to those versed in discrete probability theory. For
example, one may wish to identify statistical outliers in the
temperature information given - if we had a hundred different readings
and knew that the typical verified variance is approximately 39deg for
Moscow, any figure significantly different from this would raise alarm
bells. Standard deviation would not do, since the differences are linear
and may be missed when statistically aggregating the individual
variances as the difference between the expected and actual standard
deviations would be too small - whereas the exponential nature of
variance, obtained using VARP, would quickly distort the 39deg figure
into an unlikely number, rendering it identifiable to the statistical
researcher.
SOUNDEX
Moving away from statistics, the SOUNDEX function is an interesting
example of a function that exclusively implements a third-party
specification, a proprietary algorithm developed and patented privately
nearly a hundred years ago. SOUNDEX is a function built by Microsoft to a
precise algorithmic specification. The Soundex specification is
designed for use in systems where words need to be grouped by phonic
sound rather than by spelling - for example, in ancestry and genealogy,
the surnames Smith, Smyth and Smithe are spelled differently but could
be pronounced the same. It is important for users of expert systems that
deal in phonics to be able to recognize these similarities without
complex and inefficient rule based systems to slow down the storage and
retrieval process.
A good use of Soundex could be to assist in the automatic detection
of fraud. Some time ago, I used to work as a database administrator for a
small company specializing in the provision of online gambling to US
customers. This company would use a number of weighted measures built as
stored procedures which would take many different factors, from
postcode to IP address to demographic, to make an intelligent decision
on whether a new customer signup was likely a duplicate of an existing
account, in order to help prevent fraud. Although SOUNDEX wasn't used in
this context, there would have been a strong case for inclusion as a
fuzzy matching algorithm to determine the similarity of the 'John
Smith's to the 'Johann Smythe's.
In summary, Soundex is a specification originally designed in 1918 by
Robert C. Russell and Margaret Odell, and has risen to prominence in a
number of database specifications as a preferred system for categorizing
and relating phonics. For the history of Soundex and for a more
detailed description of the variants in use today, see the links at the
bottom of the page for more information.
Example of using Soundex:
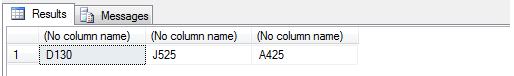
SELECT SOUNDEX('David'), SOUNDEX('Johnson'), SOUNDEX('Alison')
We could implement a SOUNDEX-based system to identify
similarly-sounding names and write a stored procedure which will
identify customer records based on matching phonics. Here's a brief
example of how it could work. Below is the build code to generate a
table with customer ID, surname and SOUNDEX code for 1000 common
surnames (you can find the list attached to this article as
sample_name_data.txt):
CREATE TABLE dbo.SoundexTest (
CustomerID INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
Surname VARCHAR(20),
Phonic VARCHAR(10) )
CREATE TABLE #surnames ( Surname VARCHAR(20) )
BULK INSERT #surnames
FROM N'c:\del\mssqltips_190213_final\sample_name_data.txt' -- replace with your path & file
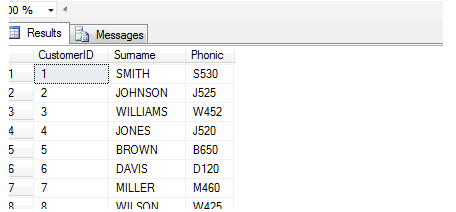
INSERT INTO dbo.SoundexTest (Surname, Phonic)
SELECT Surname, SOUNDEX(Surname)
FROM #surnames
SELECT * FROM dbo.SoundexTest
Now you could write a stored procedure to find names with similar sounds, like so:
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.checkSimilarNames ( @surname VARCHAR(20) )
AS BEGIN
DECLARE @phonic VARCHAR(10)
SET @phonic = ( SELECT TOP 1 Phonic
FROM dbo.SoundexTest
WHERE Surname = @surname )
IF @phonic IS NULL
RAISERROR('Surname not found!',10,1)
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT Surname
FROM dbo.SoundexTest
WHERE Phonic = @phonic
END
END
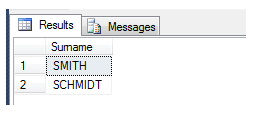
We test it like this:
EXEC dbo.checkSimilarNames @surname = 'SMITH'
With this result:
As you can see, with some development a powerful phonics comparison system can easily be built.
RANKING FUNCTIONS
The final section of this article will deal with ranking functions,
which includes the RANK, DENSE_RANK and NTILE functions and in the
author's humble opinion, underused in most SQL Server database
implementations. As a database administrator, much of my job involves
reviewing and correcting code, examining existing SQL schemas,
procedures and functions, and improving performance wherever possible.
Given the usefulness of RANK, DENSE_RANK and NTILE, I am surprised that
(at least in my experience) ranking functions are not used more often.
RANK
I have included the table build code below for your convenience:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[rankingTable](
[CustomerID] [int] NOT NULL,
[CustomerClass] [varchar](6) NULL,
[TotalDeposited] [money] NULL,
[TotalWithdrawn] [money] NULL,
[CurrentBalance] [money] NULL,
UNIQUE NONCLUSTERED
(
[CustomerID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.RankingTable (CustomerID, CustomerClass, TotalDeposited, TotalWithdrawn, CurrentBalance)
SELECT 1270, 'Bronze', 300.00, 0.00, 285.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 3243, 'Bronze', 15.00, 0.00, 122.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 4083, 'Silver', 100.00, 25.00, 255.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 2349, 'Gold', 50.00, 0.00, 47.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 9343, 'Silver', 175.00, 50.00, 22.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 5434, 'Bronze', 20.00, 0.00, 0.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 2343, 'Silver', 1500.00, 500.00, 134.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 1194, 'Gold', 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 5639, 'Bronze', 40.00, 10.00, 95.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 2030, 'Bronze', 120.00, 0.00, 105.00
UNION ALL
SELECT 3424, 'Bronze', 20.00, 0.00, 5.00
GO
Consider the following (fictional) horrible and inefficient piece of
code to rank customers in a table by £ (or $) amount gambled.
DECLARE cur_ForEachClass CURSOR LOCAL FAST_FORWARD
FOR SELECT DISTINCT CustomerClass
FROM dbo.rankingTable rt
DECLARE @class VARCHAR(6)
OPEN cur_ForEachClass
FETCH NEXT FROM cur_ForEachClass INTO @class
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @resultsTable
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerClass, TotalDeposited,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER ( ORDER BY TotalDeposited DESC ) [Ranking]
FROM dbo.rankingTable
WHERE @class = CustomerClass
FETCH NEXT FROM cur_ForEachClass INTO @class
END
SELECT * FROM @resultsTable
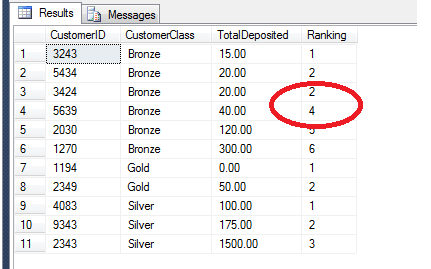
As you can see, this is inefficient and bulky. It pre-separates out
the source data into the distinct classes, orders the contents of those
classes by TotalDeposited, and glues them back together in a results
table. The output is identical to this slimline version using RANK():
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerClass, TotalDeposited,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY CustomerClass ORDER BY TotalDeposited ) AS [Ranking]
FROM dbo.rankingTable
As you can see, this is easier to read. It doesn't use a cursor and
the sorting and ordering are taken care of internally. If you're unused
to ranking functions, note that PARTITION BY x means 'partition each set
of ranks by distinct x' and ORDER BY x determines the order in which
the values must be ranked. So in the example above, PARTITION BY
CustomerClass means 'return ranks from 1 to N for each distinct class
(gold, silver, bronze)' and ORDER BY TotalDeposited DESC means '... and
the ranking should run from largest to smallest.'
DENSE_RANK
DENSE_RANK is the second main ranking function and is similar to RANK
except that gaps in the ranking are not allowed. In essence, when there
is a tie-break in the conditions for the RANK then the ranking 'skips'
one value and continues on. DENSE_RANK does not do this but continues
immediately after the tie. This is illustrated by adding another line to
our example:
INSERT INTO dbo.rankingTable VALUES ( 3424, 'Bronze', 20.00, 0.00, 5.00 );
This will insert another row with the TotalDeposited value at 20.00,
which means it will tie-break with the row with CustomerID 5434 as seen
below:
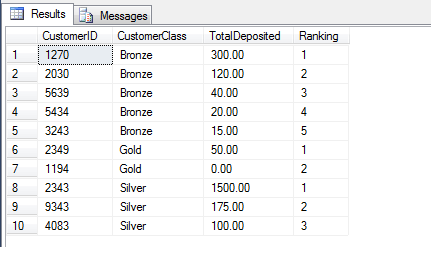
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerClass, TotalDeposited,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY CustomerClass ORDER BY TotalDeposited ) AS [Ranking]
FROM dbo.rankingTable
We can avoid this by using DENSE_RANK as follows:
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerClass, TotalDeposited,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY CustomerClass ORDER BY TotalDeposited ) AS [Ranking]
FROM dbo.rankingTable
NTILE
This brings us nicely onto NTILE. Think of NTILE as 'N'-TILE where N
refers to the 'segments' of the whole, in the same sense of the words
QUARTile or PERCENTile. This is how to use it:
SELECT CustomerID, TotalDeposited,
NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY TotalDeposited) AS [Quartile]
FROM dbo.rankingTable
In the above example, we have taken all values irrespective of player
class and returned them in the specified order, arranged into
evenly-distributed groups. We may therefore use this data to say,
'Players 1194, 3243 and 5434 are in the top 25% of players who have
contributed the most money to our enterprise'. This function is very
useful when e.g. computing performance on a bell curve
(evenly-distributed curve). The definition according to BOL may make
more sense here:
NTILE can therefore be useful when, for example, creating procedures
that execute groups of statements in batch, or when you wish to
aggregate financial figures.